

Community Forest Management
Community Forest Management:
Shared Spaces, Shared Responsibilities
In the realm of environmental conservation and sustainable natural resource management, community forest management stands out as a beacon of participatory governance and local stewardship. This approach empowers communities to collectively manage and benefit from forest resources, fostering environmental sustainability, social equity, and economic development.
From indigenous territories to rural villages, community forest management initiatives demonstrate the power of collaboration, traditional knowledge, and grassroots action in safeguarding forests and enhancing livelihoods.
Key Insight
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the dynamic world of community forest management, exploring its principles, practices, benefits, challenges, and conservation implications.
About Community Forest Management Community forest management entails the collective management and utilization of forest resources by local communities, indigenous peoples, or stakeholders with vested interests in forest lands.
This approach involves collaborative decision-making, resource sharing, and adaptive management practices that balance ecological conservation with socio-economic development objectives.
Community forest management initiatives vary in scale, scope, and governance structures, reflecting the diverse cultural, social, and ecological contexts of each community.
Types of Community Forest Management
Definition: Community forest management can be defined as the collaborative management and governance of forest resources by local communities, indigenous peoples, or stakeholders with vested interests in forest lands. This approach emphasizes participatory decision-making, equitable benefit-sharing, and sustainable use of forest resources to achieve environmental, social, and economic objectives.

Important Facts About Community Forest Management
- Community forest management empowers local communities to secure tenure rights, regulate access, and manage forest resources according to their needs, priorities, and cultural values, promoting environmental sustainability, social equity, and economic development.
- Participatory approaches in forest management enhance transparency, accountability, and legitimacy by involving local communities, stakeholders, and users in decision-making processes, resource allocation, and conflict resolution.
- Community forest management initiatives have been successful in conserving biodiversity, restoring degraded lands, and improving livelihoods, particularly in areas where traditional knowledge, social capital, and local institutions are strong.
- Sustainable forest management practices, such as selective logging, agroforestry, and fire management, promote forest regeneration, ecosystem resilience, and carbon sequestration, contributing to climate change mitigation and adaptation.
- Community forest management fosters social cohesion, cultural identity, and self-determination among local communities, empowering them to assert their rights, preserve cultural heritage, and adapt to changing socio-economic and environmental conditions.
Geographical Location of Community Forest Management: Community forest management initiatives are implemented in diverse geographic regions, including tropical forests, temperate woodlands, and drylands, spanning continents, countries, and landscapes.
From remote rural areas to peri-urban settlements, community forest management thrives in regions where local communities have a strong connection to forests, rely on forest resources for their livelihoods, and possess traditional knowledge and governance systems.
Countries with high forest cover and significant indigenous populations, such as Brazil, Indonesia, and India, are hotspots for community forest management initiatives, driven by the recognition of indigenous rights, decentralization reforms, and participatory approaches to natural resource management.
Importance of Community Forest Management
- Environmental Conservation: Community forest management promotes environmental sustainability by conserving biodiversity, protecting watersheds, and restoring degraded lands, contributing to ecosystem resilience, carbon sequestration, and climate change mitigation.
- Socio-economic Development: Community forest management enhances livelihoods, food security, and income generation for local communities by providing access to forest resources, employment opportunities, and alternative livelihoods, reducing poverty and dependence on external aid.
- Cultural Preservation: Community forest management preserves cultural heritage, traditional knowledge, and customary practices associated with forest stewardship, strengthening cultural identity, social cohesion, and intergenerational transmission of indigenous wisdom.
- Empowerment and Governance: Community forest management empowers local communities to assert their rights, participate in decision-making processes, and hold governments and other stakeholders accountable for sustainable forest management, promoting democratic governance, social justice, and human rights.
- Resilience and Adaptation: Community forest management builds resilience to environmental shocks and socio-economic pressures by diversifying livelihoods, enhancing adaptive capacity, and fostering community cohesion and solidarity, enabling communities to cope with change and uncertainty.

Development Strategies for Community Forest Management
- Capacity Building and Empowerment: Strengthen the capacity of local communities, indigenous peoples, and stakeholders to participate in community forest management through training, education, technical assistance, and institutional support, building skills, knowledge, and confidence for effective governance and stewardship.
- Legal Recognition and Tenure Reform: Secure legal recognition of community forest rights, land tenure, and customary land tenure systems through policy reforms, legislative reforms, and advocacy campaigns, ensuring equitable access to forest resources, protection of indigenous rights, and recognition of traditional knowledge and governance systems.
- Participatory Planning and Decision-Making: Facilitate inclusive and participatory processes for community-based forest planning, resource mapping, and decision-making, ensuring that diverse voices, perspectives, and interests are heard and respected, fostering ownership, consensus, and legitimacy in forest governance.
- Sustainable Resource Management Practices: Promote sustainable forest management practices, such as selective logging, agroforestry, non-timber forest products, and fire management, that enhance forest regeneration, biodiversity conservation, and ecosystem services, balancing ecological, social, and economic objectives.
- Collaborative Partnerships and Networking: Foster partnerships and collaborations among local communities, government agencies, NGOs, academic institutions, and other stakeholders to share knowledge, resources, and experiences, leveraging collective action, innovation, and learning for community forest management.


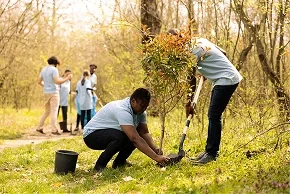
Key Insights for Learning Community Forest Management
- Community Engagement and Participation: Learn about the importance of community engagement, participation, and empowerment in community forest management, including strategies for building trust, fostering collaboration, and promoting inclusive decision-making processes.
- Traditional Knowledge and Governance Systems: Explore the role of traditional knowledge, cultural values, and indigenous governance systems in community forest management, recognizing their contributions to ecological resilience, social cohesion, and sustainable resource use.
- Policy Analysis and Advocacy: Analyze forest policies, legal frameworks, and institutional arrangements relevant to community forest management, identifying opportunities for policy reform, legislative advocacy, and institutional strengthening to support community-led conservation and sustainable development.
- Sustainable Livelihoods and Economic Development: Understand the linkages between community forest management and sustainable livelihoods, economic development, and poverty alleviation, exploring opportunities for income diversification, value addition, and market access through forest-based enterprises and sustainable resource utilization.
- Adaptive Management and Learning Networks: Embrace adaptive management approaches and learning networks that promote continuous learning, innovation, and knowledge exchange among communities, stakeholders, and practitioners, enabling adaptive responses to changing socio-economic and environmental conditions.
Threats Faced by Community Forest Management
- Land Use Conflicts and Encroachment: Competing land uses, such as agriculture, mining, infrastructure development, and urbanization, can encroach upon community forest lands, leading to land tenure conflicts, deforestation, and loss of traditional livelihoods and cultural heritage.
- Government Policies and Institutional Barriers: Inadequate recognition of community forest rights, restrictive forest policies, and bureaucratic barriers can hinder the implementation and effectiveness of community forest management initiatives, undermining local governance, autonomy, and decision-making authority.
- External Pressures and Exploitation: External pressures from logging companies, commercial interests, and external actors can exploit community forest resources, undermine local control, and exacerbate social tensions, leading to resource depletion, environmental degradation, and social conflict.
- Climate Change and Environmental Degradation: Climate change impacts, such as increased temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events, can exacerbate environmental degradation, forest fires, and habitat loss, challenging the resilience and adaptive capacity of community forest management systems.
- Socio-economic Inequalities and Power Dynamics: Socio-economic disparities, unequal access to resources, and power imbalances within and among communities can marginalize vulnerable groups, exclude marginalized voices, and perpetuate social injustices, limiting the effectiveness and equity of community forest management initiatives.
Conservation of Community Forest Management
- Legal Recognition and Tenure Reform: Advocate for legal recognition of community forest rights, land tenure security, and customary land governance systems through policy reforms, legislative advocacy, and legal empowerment initiatives, ensuring equitable access to forest resources and protection of indigenous rights.
- Capacity Building and Empowerment: Strengthen the capacity of local communities, indigenous peoples, and stakeholders to participate in community forest management through training, education, technical assistance, and institutional support, building skills, knowledge, and confidence for effective governance and stewardship.
- Participatory Governance and Decision-Making: Promote inclusive and participatory processes for community-based forest planning, management, and decision-making, ensuring that diverse voices, perspectives, and interests are heard and respected, fostering ownership, consensus, and legitimacy in forest governance.
- Sustainable Resource Management Practices: Encourage adoption of sustainable forest management practices, such as selective logging, agroforestry, and community-based conservation, that enhance forest resilience, biodiversity conservation, and ecosystem services, balancing ecological, social, and economic objectives.
- Strengthening Collaborative Partnerships: Foster partnerships and collaborations among local communities, government agencies, NGOs, academic institutions, and other stakeholders to share knowledge, resources, and experiences, leveraging collective action, innovation, and learning for community forest management.
Conclusion
Conclusion: In conclusion, community forest management offers a promising approach to conserving forests, empowering communities, and promoting sustainable development. By fostering local stewardship, participatory governance, and traditional knowledge, community forest management initiatives contribute to environmental sustainability, social equity, and economic resilience.
As we navigate the complex challenges of forest conservation and natural resource management, let us embrace the principles of community empowerment, collaboration, and adaptive management to nurture nature together and build a more sustainable and inclusive future for all.
Community Forest Management
Community forest management entails the collaborative and sustainable administration of forest resources by local residents within a designated area. This approach empowers communities to oversee forest activities, promoting conservation, livelihood enhancement, and ecological resilience.
Local Empowerment
Community forest management empowers local communities to govern and utilize forest resources according to their needs and traditional knowledge. By granting decision-making authority to those directly impacted by forest management, this approach fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility for conservation efforts.
Shared Governance
Shared governance structures, involving collaboration between community members, government agencies, and other stakeholders, are integral to effective community forest management. By fostering inclusive decision-making processes and transparent communication, shared governance ensures equitable distribution of benefits and promotes social cohesion.
Sustainable Practices
Community forest management emphasizes sustainable harvesting practices, ensuring that resource extraction does not exceed the forest's regenerative capacity. Through careful planning and monitoring, communities can maintain ecological balance, preserve biodiversity, and safeguard forest health for future generations.
Livelihood Enhancement
Community forest management supports the diversification of local livelihoods through sustainable forest-based enterprises, such as non-timber forest product collection, ecotourism, and agroforestry. By generating alternative sources of income, these initiatives reduce dependency on forest resources and improve community resilience to economic fluctuations.
Conservation Goals
Community forest management prioritizes conservation objectives, aiming to protect biodiversity, mitigate climate change, and maintain ecosystem services. By implementing conservation measures, such as habitat restoration and wildlife monitoring, communities contribute to global biodiversity conservation efforts and ecological sustainability.
Cultural Preservation
Community forest management promotes the preservation of indigenous knowledge, cultural practices, and traditional values associated with forests. By recognizing and respecting local customs and beliefs, this approach strengthens cultural identity, fosters intergenerational knowledge transfer, and enhances social cohesion within communities.
Capacity Building
Capacity building initiatives are essential for empowering communities to effectively manage forest resources and address emerging challenges. Training programs, technical support, and educational opportunities equip community members with the skills and expertise needed to implement sustainable forest management practices and adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Policy Advocacy
Community forest management advocates for supportive policies and legal frameworks that recognize and protect community tenure rights over forest resources. By engaging with policymakers and advocating for their interests, communities can secure legal recognition, secure land tenure, and access resources necessary for successful forest management.
Participatory Monitoring and Evaluation
Participatory monitoring and evaluation processes enable communities to assess the effectiveness of their forest management activities, identify areas for improvement, and adapt strategies accordingly. By engaging in collaborative monitoring efforts, communities enhance transparency, accountability, and learning outcomes, leading to more informed decision-making and improved management practices.
 OUR FAQ US
OUR FAQ USFrequently Asked Questions About Community Forest Management
What is Community Forest Management?
Community Forest Management (CFM) refers to the sustainable management and conservation of forests by local communities who have legal rights or customary tenure over forest resources. CFM involves collaborative decision-making, resource use, and benefit-sharing arrangements among community members, aimed at promoting forest conservation, livelihood improvement, and socio-economic development.
How does Community Forest Management benefit the environment?
Community Forest Management offers several environmental benefits. It promotes sustainable forest management practices, such as selective logging and agroforestry, which help maintain forest cover, biodiversity, and ecosystem services. CFM initiatives also contribute to carbon sequestration, soil conservation, watershed protection, and wildlife habitat preservation.
Where are Community Forest Management initiatives typically implemented?
Community Forest Management initiatives are implemented in various forested landscapes globally, including tropical rainforests, boreal forests, and temperate woodlands. These initiatives are often found in regions where local communities have traditional connections to forest resources and where governments recognize community rights to forest land and resources.
How does Community Forest Management contribute to community development?
Community Forest Management contributes to community development by providing opportunities for sustainable livelihoods, income generation, and poverty alleviation. It empowers local communities to participate in decision-making processes, strengthens social cohesion and cultural identity, enhances food security through forest products and ecosystem services, and improves access to education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
What are the key principles of Community Forest Management?
Key principles of Community Forest Management include community participation and empowerment, equitable benefit-sharing, sustainable resource use, respect for indigenous knowledge and cultural values, transparent and inclusive governance structures, adaptive management practices, and collaboration with external stakeholders such as governments, NGOs, and private sector entities.
How does Community Forest Management promote biodiversity conservation?
Community Forest Management promotes biodiversity conservation by involving local communities in forest protection, monitoring, and restoration activities. CFM initiatives often incorporate traditional ecological knowledge and practices, which support the conservation of native species and ecosystems. By securing community tenure rights, CFM helps prevent deforestation, habitat degradation, and biodiversity loss.
What are the challenges associated with Community Forest Management?
Challenges associated with Community Forest Management include insecure land tenure and property rights, insufficient capacity and resources for community governance and management, conflicts over resource use and benefit-sharing, external pressures such as logging, mining, and land conversion, limited access to markets and value chains, and vulnerability to climate change impacts.
How can individuals contribute to Community Forest Management?
Individuals can contribute to Community Forest Management by supporting community-led conservation initiatives, advocating for policies that recognize and protect community forest rights, volunteering for capacity-building and training programs, promoting sustainable consumption and forest-friendly products, and engaging in dialogue and partnerships with local communities and stakeholders.
What role do governments play in supporting Community Forest Management?
Governments play a crucial role in supporting Community Forest Management by recognizing and legally securing community forest tenure rights, providing technical and financial support for capacity building and training, facilitating multi-stakeholder collaboration and conflict resolution mechanisms, integrating CFM into national forest policies and programs, and ensuring compliance with legal frameworks and international standards.
How does Community Forest Management contribute to climate change adaptation and mitigation?
Community Forest Management contributes to climate change adaptation and mitigation by enhancing forest resilience, carbon sequestration, and sustainable land management practices. CFM initiatives help reduce deforestation and forest degradation, which are significant contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, while also supporting community adaptation strategies to climate variability and extreme weather events.
Send Your Mail
 OUR CONTACT NOW
OUR CONTACT NOW
Determine You Want To Achieve
Relaxing Garden & Functional.
Business tailored design, management & support services. Business agency elit, sed do eiusmod tempor...


